总体架构
-
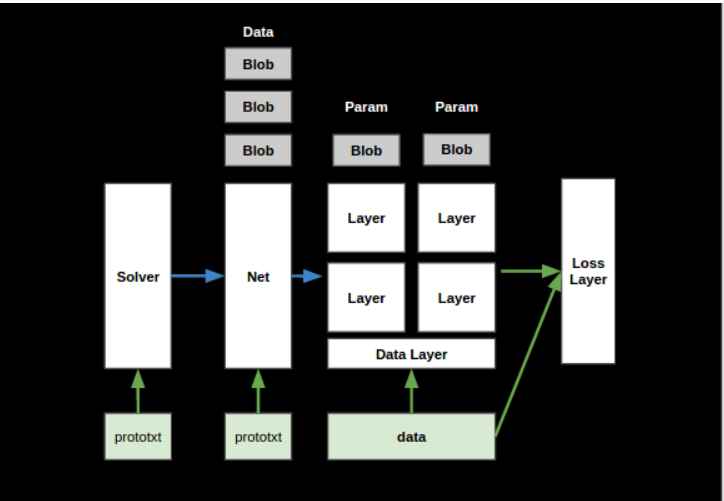
Caffe架构如下图所示,下面依次介绍主要的组件。
SyncedMemory
负责内存的分配,host和device之间的内存同步。
源码文件
include/caffe/syncedmem.hppsrc/caffe/syncedmem.cppsrc/caffe/test/test_syncedmem.cpp
成员变量
private:
void* cpu_ptr_; // 指向host内存首地址的指针,可以指向任何类型的数据
void* gpu_ptr_; // 指向device内存首地址的指针
size_t size_; // 内存占多少字节
SyncedHead head_; // 标识当前数据在什么设备上,枚举值(UNINITIALIZED,HEAD_AT_CPU,HEAD_AT_GPU,SYNCED)
bool own_cpu_data_;
bool cpu_malloc_use_cuda_;
bool own_gpu_data_;
int device_;
构造函数
初始化成员变量
SyncedMemory::SyncedMemory()
: cpu_ptr_(NULL), gpu_ptr_(NULL), size_(0), head_(UNINITIALIZED),
own_cpu_data_(false), cpu_malloc_use_cuda_(false), own_gpu_data_(false) {
#ifndef CPU_ONLY
#ifdef DEBUG
CUDA_CHECK(cudaGetDevice(&device_));
#endif
#endif
}
SyncedMemory::SyncedMemory(size_t size)
: cpu_ptr_(NULL), gpu_ptr_(NULL), size_(size), head_(UNINITIALIZED),
own_cpu_data_(false), cpu_malloc_use_cuda_(false), own_gpu_data_(false) {
#ifndef CPU_ONLY
#ifdef DEBUG
CUDA_CHECK(cudaGetDevice(&device_));
#endif
#endif
}
分配内存
cpu_data():- 如果
head_=UNINITIALIZED: 在host上分配动态内存空间,大小为size_,并全部初始化为0 - 如果
head_=HEAD_AT_GPU: 在host上分配动态内存空间(如果还没有分配的话),调用cudaMemcpy把device数据拷贝到host
- 如果
最后,返回指向host内存首地址的const指针,不能通过该指针修改其所指向的数据
const void* SyncedMemory::cpu_data() {
check_device();
to_cpu();
return (const void*)cpu_ptr_;
}
inline void SyncedMemory::to_cpu() {
...
case UNINITIALIZED:
CaffeMallocHost(&cpu_ptr_, size_, &cpu_malloc_use_cuda_);
caffe_memset(size_, 0, cpu_ptr_);
head_ = HEAD_AT_CPU;
case HEAD_AT_GPU:
if (cpu_ptr_ == NULL) {
CaffeMallocHost(&cpu_ptr_, size_, &cpu_malloc_use_cuda_);
own_cpu_data_ = true;
}
caffe_gpu_memcpy(size_, gpu_ptr_, cpu_ptr_);
head_ = SYNCED;
...
}
inline void CaffeMallocHost(void** ptr, size_t size, bool* use_cuda) {
#ifndef CPU_ONLY
if (Caffe::mode() == Caffe::GPU) {
// CUDA函数,用于在host上分配固定内存。固定内存是一种特殊类型的内存,可以在host和device之间进行快速的数据传输。
CUDA_CHECK(cudaMallocHost(ptr, size));
*use_cuda = true;
return;
}
#endif
#ifdef USE_MKL
*ptr = mkl_malloc(size ? size:1, 64);
#else
*ptr = malloc(size);
#endif
*use_cuda = false;
CHECK(*ptr) << "host allocation of size " << size << " failed";
}
mutable_cpu_data()功能和cpu_data()一致,区别是mutable_cpu_data()返回的是非const指针,可以通过该指针来修改其所指向的数据
void* SyncedMemory::mutable_cpu_data() {
check_device();
to_cpu();
head_ = HEAD_AT_CPU;
return cpu_ptr_;
}
gpu_data()、mutable_gpu_data()分配device上的内存,过程同host。调用cudaMalloc()分配device内存
const void* gpu_data();
void* mutable_gpu_data();
读写内存
写host
SyncedMemory mem(10);
void* cpu_data = mem.mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_memset(mem.size(), 1, cpu_data);
读device
SyncedMemory mem(10);
void* cpu_data = mem.mutable_cpu_data();
EXPECT_EQ(mem.head(), SyncedMemory::HEAD_AT_CPU);
caffe_memset(mem.size(), 1, cpu_data);
const void* gpu_data = mem.gpu_data();
EXPECT_EQ(mem.head(), SyncedMemory::SYNCED);
// check if values are the same
char* recovered_value = new char[10];
caffe_gpu_memcpy(10, gpu_data, recovered_value);
for (int i = 0; i < mem.size(); ++i) {
EXPECT_EQ(recovered_value[i], 1);
}
写device
SyncedMemory mem(10);
void* gpu_data = mem.mutable_gpu_data();
caffe_gpu_memset(mem.size(), 1, gpu_data);
析构函数
释放host和device上分配的动态内存
SyncedMemory::~SyncedMemory() {
check_device();
if (cpu_ptr_ && own_cpu_data_) {
CaffeFreeHost(cpu_ptr_, cpu_malloc_use_cuda_);
}
#ifndef CPU_ONLY
if (gpu_ptr_ && own_gpu_data_) {
CUDA_CHECK(cudaFree(gpu_ptr_));
}
#endif // CPU_ONLY
}
Blob
-
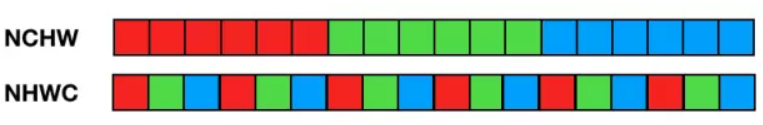
Blob是Caffe的基础数据结构,提供了统一的数据处理接口,同时隐藏了CPU/GPU异构编程的细节。Blob采用NCHW的顺序存储,也就是同一行/通道/batch的数据在内存中连续存储。因此,对于索引为(n, k, h, w)的数据,其实际索引为((n * K + k) * H + h) * W + w(K,H,W分别为通道数、高度、宽度)。
Blob是模板类,适用于不同的数据类型。
源码文件
include/caffe/blob.hppsrc/caffe/blob.cppsrc/caffe/test/test_blob.cpp
成员变量
protected:
shared_ptr<SyncedMemory> data_; // 数据,
shared_ptr<SyncedMemory> diff_; // 梯度
shared_ptr<SyncedMemory> shape_data_; // 指向 Blob 形状数据的智能指针
vector<int> shape_; // 形状
int count_; // 元素个数,也就是batch数*通道数*高度*宽度
int capacity_; // 分配的内存空间可以容纳的元素个数,必须大于等于count_
构造函数
Blob()
: data_(), diff_(), count_(0), capacity_(0) {}
template <typename Dtype>
Blob<Dtype>::Blob(const int num, const int channels, const int height, const int width)
: capacity_(0) {
Reshape(num, channels, height, width);
}
template <typename Dtype>
Blob<Dtype>::Blob(const vector<int>& shape)
: capacity_(0) {
Reshape(shape);
}
Reshape()既可以用于初始化内存分配,也可以用于调整Blob的形状。- 给
shape_data_,count_,shape_,shape_data_赋值。 - 如果
capacity_小于count_,则把data_,diff_指向新的SyncedMemory对象(还没有分配内存,lazily,有需要的时候再分配内存),同时给capacity_赋值。
- 给
template <typename Dtype>
void Blob<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<int>& shape) {
CHECK_LE(shape.size(), kMaxBlobAxes);
count_ = 1;
shape_.resize(shape.size());
// 未初始化的指针(shape_data_)为nullptr
if (!shape_data_ || shape_data_->size() < shape.size() * sizeof(int)) {
// shape_data_指向new SyncedMemory()
shape_data_.reset(new SyncedMemory(shape.size() * sizeof(int)));
}
int* shape_data = static_cast<int*>(shape_data_->mutable_cpu_data());
for (int i = 0; i < shape.size(); ++i) {
CHECK_GE(shape[i], 0);
if (count_ != 0) {
CHECK_LE(shape[i], INT_MAX / count_) << "blob size exceeds INT_MAX";
}
count_ *= shape[i];
shape_[i] = shape[i];
shape_data[i] = shape[i];
}
if (count_ > capacity_) {
capacity_ = count_;
data_.reset(new SyncedMemory(capacity_ * sizeof(Dtype)));
diff_.reset(new SyncedMemory(capacity_ * sizeof(Dtype)));
}
}
给data_,diff_分配内存
Host端:
template <typename Dtype>
const Dtype* Blob<Dtype>::cpu_data() const {
CHECK(data_);
return (const Dtype*)data_->cpu_data();
}
template <typename Dtype>
Dtype* Blob<Dtype>::mutable_cpu_data() {
CHECK(data_);
return static_cast<Dtype*>(data_->mutable_cpu_data());
}
Device端:
template <typename Dtype>
const Dtype* Blob<Dtype>::gpu_data() const {
CHECK(data_);
return (const Dtype*)data_->gpu_data();
}
template <typename Dtype>
Dtype* Blob<Dtype>::mutable_gpu_data() {
CHECK(data_);
return static_cast<Dtype*>(data_->mutable_gpu_data());
}
diff_的写法同data_:
const Dtype* cpu_diff() const;
const Dtype* gpu_diff() const;
Dtype* mutable_cpu_diff();
Dtype* mutable_gpu_diff();
Blob初始化
FillerParameter是一个protobuf消息类型,用于指定权重和偏置值的初始化方式。FillerParameter中包含以下字段:type:表示填充器类型,可选值包括 Gaussian、Xavier、Constant、MSRA 等。value:当 type 为 Constant 时,表示常量值。min和max:当 type 为 Uniform 时,表示随机均匀分布的范围。mean和std:当 type 为 Gaussian 时,表示随机高斯分布的均值和标准差。sparse:表示是否启用稀疏矩阵(Sparse Matrix)。variance_norm:表示 Xavier 填充器的方差归一化系数。
例如:UniformFiller对象接收FillerParameter参数,对blob初始化为一个随机分布。
template <typename Dtype>
void caffe_rng_uniform(const int n, const Dtype a, const Dtype b, Dtype* r) {
CHECK_GE(n, 0);
CHECK(r);
CHECK_LE(a, b);
boost::uniform_real<Dtype> random_distribution(a, caffe_nextafter<Dtype>(b));
boost::variate_generator<caffe::rng_t*, boost::uniform_real<Dtype> >
variate_generator(caffe_rng(), random_distribution);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
r[i] = variate_generator();
}
}
template <typename Dtype>
class UniformFiller : public Filler<Dtype> {
public:
explicit UniformFiller(const FillerParameter& param): Filler<Dtype>(param) {}
virtual void Fill(Blob<Dtype>* blob) {
CHECK(blob->count());
caffe_rng_uniform<Dtype>(blob->count(), Dtype(this->filler_param_.min()),
Dtype(this->filler_param_.max()), blob->mutable_cpu_data());
CHECK_EQ(this->filler_param_.sparse(), -1)
<< "Sparsity not supported by this Filler.";
}
};
FillerParameter filler_param;
UniformFiller<Dtype> filler(filler_param);
filler.Fill(this->blob);
获取Blob的信息
通过给定的位置访问数据
inline Dtype data_at(const int n, const int c, const int h,
const int w) const {
return cpu_data()[offset(n, c, h, w)];
}
inline int offset(const vector<int>& indices) const {
CHECK_LE(indices.size(), num_axes());
int offset = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num_axes(); ++i) {
offset *= shape(i);
if (indices.size() > i) {
CHECK_GE(indices[i], 0);
CHECK_LT(indices[i], shape(i));
offset += indices[i];
}
}
return offset;
}
CanonicalAxisIndex()方法可以允许用户使用负数作为索引
inline int CanonicalAxisIndex(int axis_index) const {
CHECK_GE(axis_index, -num_axes())
<< "axis " << axis_index << " out of range for " << num_axes()
<< "-D Blob with shape " << shape_string();
CHECK_LT(axis_index, num_axes())
<< "axis " << axis_index << " out of range for " << num_axes()
<< "-D Blob with shape " << shape_string();
if (axis_index < 0) {
return axis_index + num_axes();
}
return axis_index;
}
重载的shape()方法,可以返回Blob整体的形状、或者在某个轴(axis)上的维度
inline const vector<int>& shape() const { return shape_; }
inline int shape(int index) const {
return shape_[CanonicalAxisIndex(index)];
}
重载的count()方法,可以返回Blob整体的元素个数、或者从 start_axis 到 end_axis 之间的元素个数。
inline int count() const { return count_; }
inline int count(int start_axis, int end_axis) const {
CHECK_LE(start_axis, end_axis);
CHECK_GE(start_axis, 0);
CHECK_GE(end_axis, 0);
CHECK_LE(start_axis, num_axes());
CHECK_LE(end_axis, num_axes());
int count = 1;
for (int i = start_axis; i < end_axis; ++i) {
count *= shape(i);
}
return count;
}
inline int count(int start_axis) const {
return count(start_axis, num_axes());
}
序列化与反序列化
caffe使用protocol buffer来进行数据的序列化和反序列化。protobuf message是一种用于序列化和反序列化数据的数据结构,用于在不同平台和编程语言之间传输和存储数据。它定义了一种消息的结构,消息中的字段具有名称和类型,并可以嵌套和重复。通过定义消息的结构,可以将数据编码为二进制格式或文本格式,并进行跨平台和跨语言的数据交换。
caffe定义了一系列的protobuf message,在caffe.proto文件中。其中, BlobProto 来保存和读取 Blob 数据,定义如下:
message BlobProto {
optional BlobShape shape = 7;
repeated float data = 5 [packed = true];
repeated float diff = 6 [packed = true];
repeated double double_data = 8 [packed = true];
repeated double double_diff = 9 [packed = true];
// 4D dimensions -- deprecated. Use "shape" instead.
optional int32 num = 1 [default = 0];
optional int32 channels = 2 [default = 0];
optional int32 height = 3 [default = 0];
optional int32 width = 4 [default = 0];
}
ToProto()将Blob对象保存为BlobProto,分别对float和double类型做了模板特化。- 重置了
BlobProto消息类型shape,data,diff字段
- 重置了
template <>
void Blob<double>::ToProto(BlobProto* proto, bool write_diff) const {
proto->clear_shape();
for (int i = 0; i < shape_.size(); ++i) {
proto->mutable_shape()->add_dim(shape_[i]);
}
proto->clear_double_data();
proto->clear_double_diff();
const double* data_vec = cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < count_; ++i) {
proto->add_double_data(data_vec[i]);
}
if (write_diff) {
const double* diff_vec = cpu_diff();
for (int i = 0; i < count_; ++i) {
proto->add_double_diff(diff_vec[i]);
}
}
}
可以从 BlobProto 中读取 Blob 数据:
// 从文件中读取 BlobProto
caffe::BlobProto blob_proto;
caffe::ReadProtoFromBinaryFile(filename, &blob_proto);
// 将 BlobProto 转换为 Blob 对象
caffe::Blob<float> blob;
blob.FromProto(blob_proto);
数学计算
- 底层调用的是
CBLAS库和CUBLAS的方法。
/// @brief Compute the sum of absolute values (L1 norm) of the data.
Dtype asum_data() const;
template <>
float caffe_cpu_asum<float>(const int n, const float* x) {
return cblas_sasum(n, x, 1);
}
template <>
void caffe_gpu_asum<float>(const int n, const float* x, float* y) {
CUBLAS_CHECK(cublasSasum(Caffe::cublas_handle(), n, x, 1, y));
}
/// @brief Compute the sum of squares (L2 norm squared) of the data.
Dtype sumsq_data() const;
template <>
double caffe_cpu_strided_dot<double>(const int n, const double* x,
const int incx, const double* y, const int incy) {
return cblas_ddot(n, x, incx, y, incy);
}
template <>
void caffe_gpu_dot<float>(const int n, const float* x, const float* y,
float* out) {
CUBLAS_CHECK(cublasSdot(Caffe::cublas_handle(), n, x, 1, y, 1, out));
}
/// @brief Scale the blob data by a constant factor.
void scale_data(Dtype scale_factor);
template <>
void caffe_scal<float>(const int N, const float alpha, float *X) {
cblas_sscal(N, alpha, X, 1);
}
template <>
void caffe_gpu_scal<float>(const int N, const float alpha, float *X) {
CUBLAS_CHECK(cublasSscal(Caffe::cublas_handle(), N, &alpha, X, 1));
}
禁止拷贝构造和赋值拷贝
#define DISABLE_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(classname)
private:
classname(const classname&);
classname& operator=(const classname&)
参考资料
- https://github.com/BVLC/caffe
- https://hqli.github.io/doc/experience/caffe_code/index.html
- Caffe: Convolutional Architecture for Fast Feature Embedding
