Layer_factory
源码文件
include/caffe: layer_factory.hppsrc/caffe: layer_factory.cpp
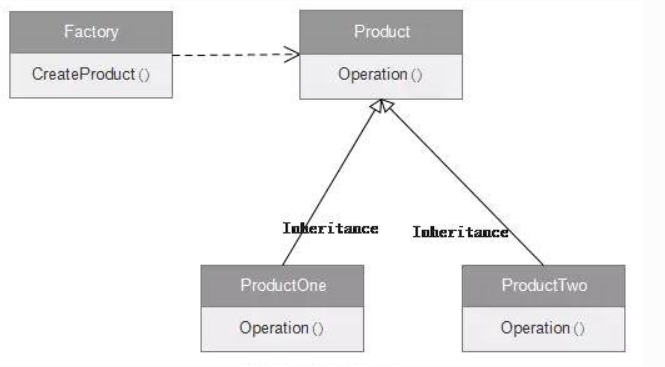
工厂模式
-
layer.hpp中的Layer类是总的产品标准,使用virtual修饰函数,layer文件夹中的PoolingLayer、ConcatLayer等类继承Layer类,是Layer类的不同实现。然后layer_factory.hpp中的LayerRegistry类实现了Layer的注册,根据层的名称然后new对应的类返回Layer类型。至此,工厂模式流程完成。优点是实例化不同的Layer类时,具有统一的接口。
LayerRegistry
- 定义了两个类型别名:
Creator: 函数指针,输入是LayerParameter,返回是shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> >CreatorRegistry: 即注册表,是一个字典,key是Layer的名称,value是Creator
public:
typedef shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> > (*Creator)(const LayerParameter&);
typedef std::map<string, Creator> CreatorRegistry;
注册Layer
有两种方式,一种是layer可以由其构造函数直接生成,那么可以在具体layer的源文件中(例如clip.cpp), 使用宏:
REGISTER_LAYER_CLASS(clip)
REGISTER_LAYER_CLASS定义了一个Creator_clipLayer的函数,然后调用宏REGISTER_LAYER_CREATOR。
\#define REGISTER_LAYER_CLASS(type)
template <typename Dtype>
shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> > Creator_##type##Layer(const LayerParameter& param)
{
return shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> >(new type##Layer<Dtype>(param));
}
REGISTER_LAYER_CREATOR(type, Creator_##type##Layer)
REGISTER_LAYER_CREATOR实例化LayerRegisterer对象。LayerRegisterer的构造函数调用LayerRegistry的AddCreator方法。
\#define REGISTER_LAYER_CREATOR(type, creator)
static LayerRegisterer<float> g_creator_f_##type(#type, creator<float>);
static LayerRegisterer<double> g_creator_d_##type(#type, creator<double>)
template <typename Dtype>
class LayerRegisterer {
public:
LayerRegisterer(const string& type,
shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> > (*creator)(const LayerParameter&)) {
// LOG(INFO) << "Registering layer type: " << type;
LayerRegistry<Dtype>::AddCreator(type, creator);
}
};
AddCreator方法调用Registry方法,Registry方法会返回一个静态成员变量CreatorRegistry(即注册表)的指针,最终把(clip,Creator_clipLayer)注册到注册表。
static CreatorRegistry& Registry() {
static CreatorRegistry* g_registry_ = new CreatorRegistry();
return *g_registry_;
}
// Adds a creator.
static void AddCreator(const string& type, Creator creator) {
CreatorRegistry& registry = Registry();
CHECK_EQ(registry.count(type), 0)
<< "Layer type " << type << " already registered.";
registry[type] = creator;
}
第二种方式,layer需要通过一个creator function来生成。那么可以在layer_factory.cpp中调用宏REGISTER_LAYER_CREATOR,来进行注册。例如:
REGISTER_LAYER_CREATOR(Convolution, GetConvolutionLayer);
生成Layer
输入LayerParameter,查找注册表,返回shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> >
LayerRegistry<Dtype>::CreateLayer(param);
static shared_ptr<Layer<Dtype> > CreateLayer(const LayerParameter& param) {
if (Caffe::root_solver()) {
LOG(INFO) << "Creating layer " << param.name();
}
const string& type = param.type();
CreatorRegistry& registry = Registry();
CHECK_EQ(registry.count(type), 1) << "Unknown layer type: " << type
<< " (known types: " << LayerTypeListString() << ")";
return registry[type](param);
}
单例模式
构造函数设为private,LayerRegisterer不能通过构造函数进行构造,从而保证只能有一个实例
private:
LayerRegistry() {}
Tanh layer
以tanh layer为例,讲解一下layer层的具体实现。
tanh layer继承自NeuronLayer, NeuronLayer接收一个blob作为参数,输出一个相同size的blob。适合的layer有Relu,Sigmoid,Elu,dropout等。NeuronLayer继承自Layer类,Layer 类提供了网络层的基本功能和接口,包括前向传播、反向传播等。
源码文件
include/caffe: layer.hpp, layer/*.hppsrc/caffe: layer.cpp, layer/*.cpp,layer/*.cu
初始化输入Blob
FillerParameter filler_param;
filler_param.set_std(filler_std);
GaussianFiller<Dtype> filler(filler_param);
filler.Fill(this->blob_bottom_);
构造Tanh Layer
LayerParameter layer_param;
TanHLayer<Dtype> layer(layer_param);
构造函数在基类实现,初始化layer_param_,phase_, blobs_。
explicit Layer(const LayerParameter& param)
: layer_param_(param) {
// Set phase and copy blobs (if there are any).
phase_ = param.phase();
if (layer_param_.blobs_size() > 0) {
blobs_.resize(layer_param_.blobs_size());
for (int i = 0; i < layer_param_.blobs_size(); ++i) {
blobs_[i].reset(new Blob<Dtype>());
blobs_[i]->FromProto(layer_param_.blobs(i));
}
}
}
成员变量
layer_param_:LayerParameter是用于描述Layer的protobuf消息类型,包含的主要字段有:type: The type of layer, such asConvolution,Pooling,ReLU, etc.name: The name of the layer, which can be used to identify it in the network.bottom: The name(s) of the input blobs for the layer.top: The name(s) of the output blobs for the layer.include: Specifies which phases (TRAIN or TEST) the layer should be included in.param: A repeated field containing the hyperparameters for the layer.blobs: A repeated field containing the weight and bias parameters for the layer.Layer type-specific parameters: e.g.ConvolutionParameter,BatchNormParameter,InnerProductParameter…
phase_: 标识网络的运行阶段:TRAINorTEST。TRAIN Phase用于训练网络,它会根据损失函数计算的梯度来更新网络的权重。在TRAIN Phase中,通常会使用一些数据增强技术(如随机裁剪、随机翻转等)来扩充训练数据集。TEST Phase用于测试和评估网络的性能。在TEST Phase中,网络通常不进行权重更新,并且使用整个测试数据集进行测试,以计算网络在给定任务上的精度和损失。
blobs_:Layer的权重和偏置,也就是模型要学习的参数,weight和bias分开保存在两个blob中param_propagate_down_: 存储参数更新的开关,即是否对层的参数进行反向传播更新。它是一个bool类型的向量,长度等于blobs_向量的长度,每个元素表示对应的Blob是否需要进行参数更新。loss_: vector类型,每个top blob是否有非零的权重weight
protected:
/** The protobuf that stores the layer parameters */
LayerParameter layer_param_;
/** The phase: TRAIN or TEST */
Phase phase_;
/** The vector that stores the learnable parameters as a set of blobs. */
vector<shared_ptr<Blob<Dtype> > > blobs_;
/** Vector indicating whether to compute the diff of each param blob. */
vector<bool> param_propagate_down_;
/** The vector that indicates whether each top blob has a non-zero weight in
* the objective function. */
vector<Dtype> loss_;
SetUp()
- 校验输入&输出的
Blob数量是否正确 - 初始化
blobs_,param_propagate_down_ - 调整输出
Blob的形状 - 设置loss的权重
void SetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
CheckBlobCounts(bottom, top);
LayerSetUp(bottom, top);
Reshape(bottom, top);
SetLossWeights(top);
}
前向传播
layer.Forward(this->blob_bottom_vec_, this->blob_top_vec_);
template <typename Dtype>
void TanHLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
const int count = bottom[0]->count();
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
top_data[i] = tanh(bottom_data[i]);
}
}
还有GPU实现:
template <typename Dtype>
__global__ void TanHForward(const int n, const Dtype* in, Dtype* out) {
CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, n) {
out[index] = tanh(in[index]);
}
}
template <typename Dtype>
void TanHLayer<Dtype>::Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->gpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_gpu_data();
const int count = bottom[0]->count();
// NOLINT_NEXT_LINE(whitespace/operators)
TanHForward<Dtype><<<CAFFE_GET_BLOCKS(count), CAFFE_CUDA_NUM_THREADS>>>(
count, bottom_data, top_data);
CUDA_POST_KERNEL_CHECK;
}
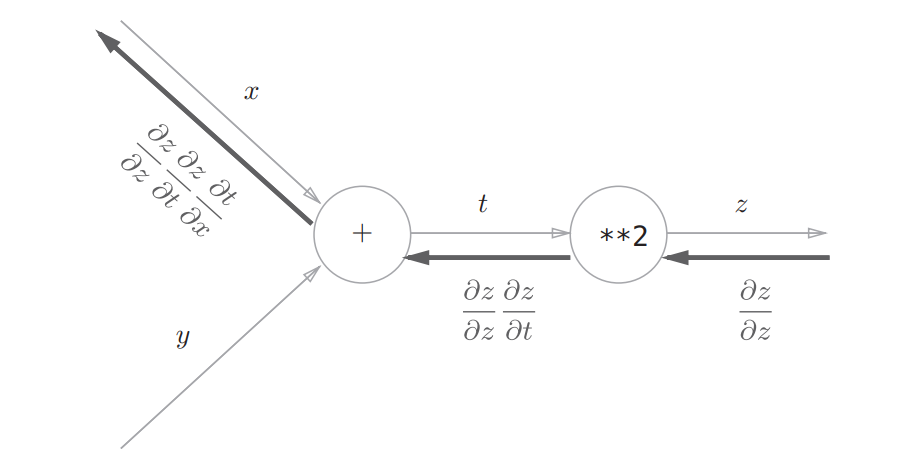
反向传播
-
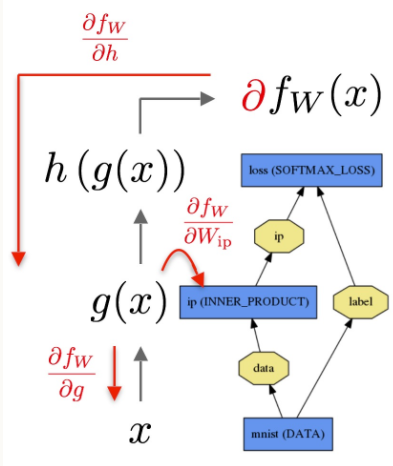
通过SGD等方法优化神经网络参数,需要计算神经网络参数关于误差的梯度。这可以通过反向传播得到,也就是沿着前向传播相反的方向,乘上局部导数,起始点是误差关于输出值的偏导数。反向传播是基于链式法则的,计算过程需要用到前向传播得到的中间结果。
Backward()实现了反向传播,也就是给定top blob和error gradient计算得到bottom的error gradient。其输入是 top blobs ,在top blobs里面的diff存储的就是其相应的error gradients。其中propagate_down这个参数跟Bottom的长度是一样的,每一个Index用来指定是否需要反向传播error gradients 到对应的bottom blob。而bottom 这里面的diff 区域存放的就是BackWard计算出来相应的gradient error。
如果自己你要实现一个自己的Layer,主要实现的就是Forward_cpu和Backward_cpu 以及gpu(可选)。
可以参考何凯明的深度残差网络
tanh的反向传播公式:
# 求导
dtanh = 1 - tanh^2(x)
# 链式法则
grad_x = grad_y * dtanh = grad_y * (1 - tanh^2(x))
CPU实现:
template <typename Dtype>
void TanHLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
if (propagate_down[0]) {
const Dtype* top_data = top[0]->cpu_data();
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff();
const int count = bottom[0]->count();
Dtype tanhx;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
tanhx = top_data[i];
bottom_diff[i] = top_diff[i] * (1 - tanhx * tanhx);
}
}
}
GPU实现:
template <typename Dtype>
__global__ void TanHBackward(const int n, const Dtype* in_diff,
const Dtype* out_data, Dtype* out_diff) {
CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, n) {
Dtype tanhx = out_data[index];
out_diff[index] = in_diff[index] * (1 - tanhx * tanhx);
}
}
template <typename Dtype>
void TanHLayer<Dtype>::Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
if (propagate_down[0]) {
const Dtype* top_data = top[0]->gpu_data();
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->gpu_diff();
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[0]->mutable_gpu_diff();
const int count = bottom[0]->count();
// NOLINT_NEXT_LINE(whitespace/operators)
TanHBackward<Dtype><<<CAFFE_GET_BLOCKS(count), CAFFE_CUDA_NUM_THREADS>>>(
count, top_diff, top_data, bottom_diff);
CUDA_POST_KERNEL_CHECK;
}
}
InnerProduct Layer
前向传播
- 输入数据(N×C×H×W )首先被展开成 N×D 的二维矩阵,其中 D=C×H×W。
- 该二维矩阵与一个大小为 D×M 的权重矩阵 W 相乘,得到一个大小为 N×M 的矩阵。
- 该矩阵的每一行都加上一个大小为 M 的偏置向量 b。
- 最后输出一个大小为 N×M 的矩阵。
template<>
void caffe_cpu_gemm<float>(const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransA,
const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransB, const int M, const int N, const int K,
const float alpha, const float* A, const float* B, const float beta,
float* C) {
int lda = (TransA == CblasNoTrans) ? K : M;
int ldb = (TransB == CblasNoTrans) ? N : K;
cblas_sgemm(CblasRowMajor, TransA, TransB, M, N, K, alpha, A, lda, B,
ldb, beta, C, N);
}
template <typename Dtype>
void InnerProductLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data();
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, transpose_ ? CblasNoTrans : CblasTrans,
M_, N_, K_, (Dtype)1.,
bottom_data, weight, (Dtype)0., top_data);
if (bias_term_) {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, M_, N_, 1, (Dtype)1.,
bias_multiplier_.cpu_data(),
this->blobs_[1]->cpu_data(), (Dtype)1., top_data);
}
}
GPU实现:
template <>
void caffe_gpu_gemm<float>(const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransA,
const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransB, const int M, const int N, const int K,
const float alpha, const float* A, const float* B, const float beta,
float* C) {
// Note that cublas follows fortran order.
int lda = (TransA == CblasNoTrans) ? K : M;
int ldb = (TransB == CblasNoTrans) ? N : K;
cublasOperation_t cuTransA =
(TransA == CblasNoTrans) ? CUBLAS_OP_N : CUBLAS_OP_T;
cublasOperation_t cuTransB =
(TransB == CblasNoTrans) ? CUBLAS_OP_N : CUBLAS_OP_T;
CUBLAS_CHECK(cublasSgemm(Caffe::cublas_handle(), cuTransB, cuTransA,
N, M, K, &alpha, B, ldb, A, lda, &beta, C, N));
}
template <typename Dtype>
void InnerProductLayer<Dtype>::Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->gpu_data();
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_gpu_data();
const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[0]->gpu_data();
if (M_ == 1) {
caffe_gpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, N_, K_, (Dtype)1.,
weight, bottom_data, (Dtype)0., top_data);
if (bias_term_)
caffe_gpu_axpy<Dtype>(N_, bias_multiplier_.cpu_data()[0],
this->blobs_[1]->gpu_data(), top_data);
} else {
caffe_gpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans,
transpose_ ? CblasNoTrans : CblasTrans,
M_, N_, K_, (Dtype)1.,
bottom_data, weight, (Dtype)0., top_data);
if (bias_term_)
caffe_gpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, M_, N_, 1, (Dtype)1.,
bias_multiplier_.gpu_data(),
this->blobs_[1]->gpu_data(), (Dtype)1., top_data);
}
}
反向传播
计算梯度:
dx = dy * W^T
dW = x^T * dy
db = sum(dy, axis=0)
template <typename Dtype>
void InnerProductLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
if (this->param_propagate_down_[0]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
// Gradient with respect to weight
if (transpose_) {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasTrans, CblasNoTrans,
K_, N_, M_,
(Dtype)1., bottom_data, top_diff,
(Dtype)1., this->blobs_[0]->mutable_cpu_diff());
} else {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasTrans, CblasNoTrans,
N_, K_, M_,
(Dtype)1., top_diff, bottom_data,
(Dtype)1., this->blobs_[0]->mutable_cpu_diff());
}
}
if (bias_term_ && this->param_propagate_down_[1]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
// Gradient with respect to bias
caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasTrans, M_, N_, (Dtype)1., top_diff,
bias_multiplier_.cpu_data(), (Dtype)1.,
this->blobs_[1]->mutable_cpu_diff());
}
if (propagate_down[0]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->cpu_diff();
// Gradient with respect to bottom data
if (transpose_) {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasTrans,
M_, K_, N_,
(Dtype)1., top_diff, this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data(),
(Dtype)0., bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff());
} else {
caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans,
M_, K_, N_,
(Dtype)1., top_diff, this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data(),
(Dtype)0., bottom[0]->mutable_cpu_diff());
}
}
}
template <typename Dtype>
void InnerProductLayer<Dtype>::Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
const vector<bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
if (this->param_propagate_down_[0]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->gpu_diff();
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->gpu_data();
// Gradient with respect to weight
if (transpose_) {
caffe_gpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasTrans, CblasNoTrans,
K_, N_, M_,
(Dtype)1., bottom_data, top_diff,
(Dtype)1., this->blobs_[0]->mutable_gpu_diff());
} else {
caffe_gpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasTrans, CblasNoTrans,
N_, K_, M_,
(Dtype)1., top_diff, bottom_data,
(Dtype)1., this->blobs_[0]->mutable_gpu_diff());
}
}
if (bias_term_ && this->param_propagate_down_[1]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->gpu_diff();
// Gradient with respect to bias
caffe_gpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasTrans, M_, N_, (Dtype)1., top_diff,
bias_multiplier_.gpu_data(), (Dtype)1.,
this->blobs_[1]->mutable_gpu_diff());
}
if (propagate_down[0]) {
const Dtype* top_diff = top[0]->gpu_diff();
// Gradient with respect to bottom data
if (transpose_) {
caffe_gpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasTrans,
M_, K_, N_,
(Dtype)1., top_diff, this->blobs_[0]->gpu_data(),
(Dtype)0., bottom[0]->mutable_gpu_diff());
} else {
caffe_gpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans,
M_, K_, N_,
(Dtype)1., top_diff, this->blobs_[0]->gpu_data(),
(Dtype)0., bottom[0]->mutable_gpu_diff());
}
}
}
参考资料
- https://github.com/BVLC/caffe
- https://hqli.github.io/doc/experience/caffe_code/index.html