Philosophy
- Expression: models and optimizations are defined as plaintext schemas instead of code.
- Speed: for research and industry alike speed is crucial for state-of-the-art models and massive data.
- Modularity: new tasks and settings require flexibility and extension.
- Openness: scientific and applied progress call for common code, reference models, and reproducibility.
- Community: academic research, startup prototypes, and industrial applications all share strength by joint discussion and development in a BSD-2 project.
主要概念
Blob
-
Blob是Caffe的基础数据结构,提供了统一的数据处理接口,同时隐藏了CPU/GPU异构编程的细节。Bolb底层是按照行优先存储(C-contiguous)的多维数组。Blob采用NCHW的顺序存储,也就是同一行/通道/batch的数据在内存中连续存储。因此,对于索引为(n, k, h, w)的数据,其实际索引为((n * K + k) * H + h) * W + w(K,H,W分别为通道数、高度、宽度)。
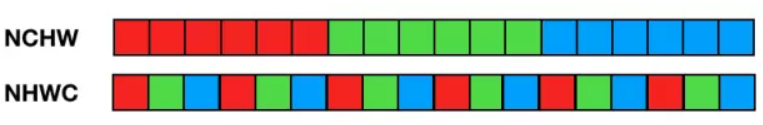
实现细节
在深度学习中,我们通常关心数据的值和梯度值。因此Blob中分别存储了这两部分数据:data,diff。
Blob提供了两种访问数据的方法:const方法不会改变数据,mutable方法会改变数据。
const Dtype* cpu_data() const;
Dtype* mutable_cpu_data();
如果你不想改变数据的值,建议使用const方法,同时通过函数来访问指针。
Blob通过SyncedMem类来同步CPU和GPU之间的数据。当需要使用GPU时,首先通过CPU指令把数据加载到blob对象,然后调用GPU kernel来执行计算,如果神经网络的所有层都有GPU实现,那么中间数据和梯度都保留在GPU显存中,计算结束,再返回到主存。
下面一些例子,可以帮助我们理解数据什么时候会发生拷贝:
// Assuming that data are on the CPU initially, and we have a blob.
const Dtype* foo;
Dtype* bar;
foo = blob.gpu_data(); // data copied cpu->gpu.
foo = blob.cpu_data(); // no data copied since both have up-to-date contents.
bar = blob.mutable_gpu_data(); // no data copied.
// ... some operations ...
bar = blob.mutable_gpu_data(); // no data copied when we are still on GPU.
foo = blob.cpu_data(); // data copied gpu->cpu, since the gpu side has modified the data
foo = blob.gpu_data(); // no data copied since both have up-to-date contents
bar = blob.mutable_cpu_data(); // still no data copied.
bar = blob.mutable_gpu_data(); // data copied cpu->gpu.
bar = blob.mutable_cpu_data(); // data copied gpu->cpu.
Layer
-
Layer是神经网络的基本单元,包括卷积、pooling、点乘、relu、sigmoid等。
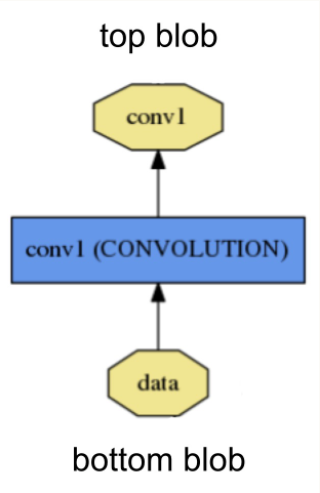
Layer类包含三个关键的步骤:- Setup: initialize the layer and its connections once at model initialization.
- Forward: given input from bottom compute the output and send to the top.
- Backward: given the gradient w.r.t. the top output compute the gradient w.r.t. to the input and send to the bottom. A layer with parameters computes the gradient w.r.t. to its parameters and stores it internally.
其中,Forward和Backward有CPU和GPU两个实现版本。
Net
-
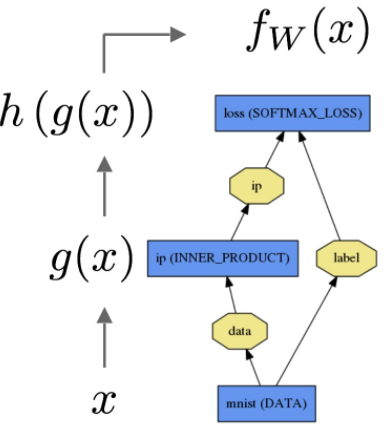
Net即神经网络,将Layer连接形成计算图,计算图是一个有向无环图(DAG),Caffe中神经网络的定义非常直观,下图是一个简单的逻辑回归分类器
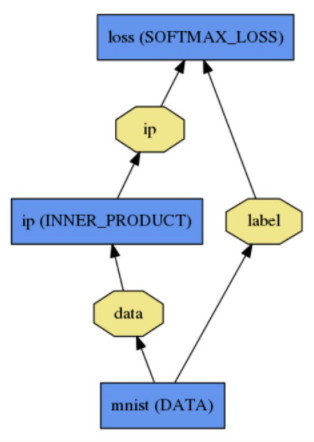
其网络定义如下:
name: "LogReg"
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
data_param {
source: "input_leveldb"
batch_size: 64
}
}
layer {
name: "ip"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "data"
top: "ip"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "ip"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}
- 模型通过
Net::Init()进行初始化:- 创建
blobs和layers来搭建计算图 - 调用
layers的setup()方法 - 校验模型结构的正确性
- 打印初始化日志
- 创建
I0902 22:52:17.931977 2079114000 net.cpp:39] Initializing net from parameters:
name: "LogReg"
[...model prototxt printout...]
# construct the network layer-by-layer
I0902 22:52:17.932152 2079114000 net.cpp:67] Creating Layer mnist
I0902 22:52:17.932165 2079114000 net.cpp:356] mnist -> data
I0902 22:52:17.932188 2079114000 net.cpp:356] mnist -> label
I0902 22:52:17.932200 2079114000 net.cpp:96] Setting up mnist
I0902 22:52:17.935807 2079114000 data_layer.cpp:135] Opening leveldb input_leveldb
I0902 22:52:17.937155 2079114000 data_layer.cpp:195] output data size: 64,1,28,28
I0902 22:52:17.938570 2079114000 net.cpp:103] Top shape: 64 1 28 28 (50176)
I0902 22:52:17.938593 2079114000 net.cpp:103] Top shape: 64 (64)
I0902 22:52:17.938611 2079114000 net.cpp:67] Creating Layer ip
I0902 22:52:17.938617 2079114000 net.cpp:394] ip <- data
I0902 22:52:17.939177 2079114000 net.cpp:356] ip -> ip
I0902 22:52:17.939196 2079114000 net.cpp:96] Setting up ip
I0902 22:52:17.940289 2079114000 net.cpp:103] Top shape: 64 2 (128)
I0902 22:52:17.941270 2079114000 net.cpp:67] Creating Layer loss
I0902 22:52:17.941305 2079114000 net.cpp:394] loss <- ip
I0902 22:52:17.941314 2079114000 net.cpp:394] loss <- label
I0902 22:52:17.941323 2079114000 net.cpp:356] loss -> loss
# set up the loss and configure the backward pass
I0902 22:52:17.941328 2079114000 net.cpp:96] Setting up loss
I0902 22:52:17.941328 2079114000 net.cpp:103] Top shape: (1)
I0902 22:52:17.941329 2079114000 net.cpp:109] with loss weight 1
I0902 22:52:17.941779 2079114000 net.cpp:170] loss needs backward computation.
I0902 22:52:17.941787 2079114000 net.cpp:170] ip needs backward computation.
I0902 22:52:17.941794 2079114000 net.cpp:172] mnist does not need backward computation.
# determine outputs
I0902 22:52:17.941800 2079114000 net.cpp:208] This network produces output loss
# finish initialization and report memory usage
I0902 22:52:17.941810 2079114000 net.cpp:467] Collecting Learning Rate and Weight Decay.
I0902 22:52:17.941818 2079114000 net.cpp:219] Network initialization done.
I0902 22:52:17.941824 2079114000 net.cpp:220] Memory required for data: 201476
模型格式
Caffe的模型定义采用纯文本的prototxt格式(.prototxt),训练好的模型序列化成protocol buffer文件(.caffemodel )。
caffe.proto文件定义了用于定义神经网络的消息的结构。
Forward & Backward
-
神经网络的计算过程由Forward和Backword组成:
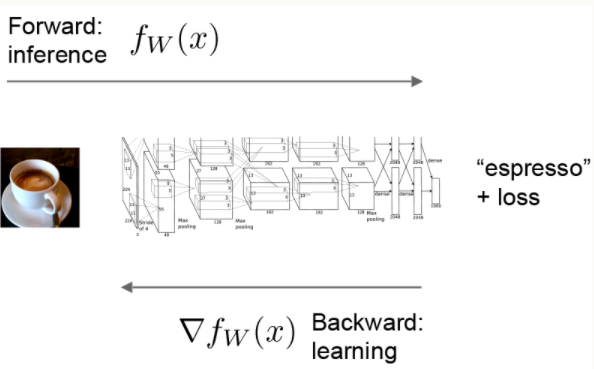
-
Foward阶段按照计算图中Layer的顺序,对输入数据进行前向推导
-
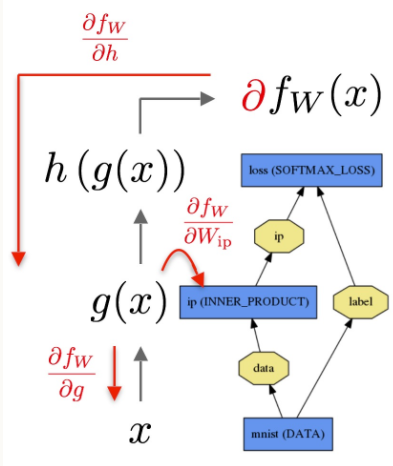
Backward阶段通过自动微分(automatic differentiation)将梯度进行反向传播,通过链式法则计算每一层的梯度。
Loss
Loss定义了目标和预测值的差距,神经网络参数学习的目标是最小化Loss,通过 Forward pass 计算Loss。下面是SoftmaxWithLoss的定义:
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "pred"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}
Solver
Solver根据Net生成的loss和gradients,决定如何更新参数。Caffe提供的Solver有:- Stochastic Gradient Descent (
type: "SGD"), - AdaDelta (
type: "AdaDelta"), - Adaptive Gradient (
type: "AdaGrad"), - Adam (
type: "Adam"), - Nesterov’s Accelerated Gradient (
type: "Nesterov") and - RMSprop (
type: "RMSProp")
- Stochastic Gradient Descent (
- 每一步的迭代过程是这样的:
- calls network forward to compute the output and loss
- calls network backward to compute the gradients
- incorporates the gradients into parameter updates according to the solver method
- updates the solver state according to learning rate, history, and method
Data
Data Layer负责加载数据成Blob,数据转换,输出数据。
layer {
name: "mnist"
# Data layer loads leveldb or lmdb storage DBs for high-throughput.
type: "Data"
# the 1st top is the data itself: the name is only convention
top: "data"
# the 2nd top is the ground truth: the name is only convention
top: "label"
# the Data layer configuration
data_param {
# path to the DB
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb"
# type of DB: LEVELDB or LMDB (LMDB supports concurrent reads)
backend: LMDB
# batch processing improves efficiency.
batch_size: 64
}
# common data transformations
transform_param {
# feature scaling coefficient: this maps the [0, 255] MNIST data to [0, 1]
scale: 0.00390625
}
}
Caffe如何计算卷积
采用img2col的方法,优点是把卷积运算变成了一个矩阵乘法问题,而矩阵乘法业界已经进行了大量优化(BLAS Libraries),缺点是内存开销大。因此只是一个临时方案,有优化空间。
Interfaces
Caffe 提供了command line,Python,Matlab接口,方便不同的开发者。
Command Line
使用cmdcaffe工具可以在命令行进行模型的训练、评估等
gflags解析命令行参数
DEFINE_string(gpu, "",
"Optional; run in GPU mode on given device IDs separated by ','."
"Use '-gpu all' to run on all available GPUs. The effective training "
"batch size is multiplied by the number of devices.");
::gflags::ParseCommandLineFlags(pargc, pargv, true);
caffe command function
通过定义宏进行注册
// A simple registry for caffe commands.
typedef int (*BrewFunction)();
typedef std::map<caffe::string, BrewFunction> BrewMap;
BrewMap g_brew_map;
#define RegisterBrewFunction(func) \
namespace { \
class __Registerer_##func { \
public: /* NOLINT */ \
__Registerer_##func() { \
g_brew_map[#func] = &func; \
} \
}; \
__Registerer_##func g_registerer_##func; \
}
RegisterBrewFunction(device_query);
RegisterBrewFunction(train);
RegisterBrewFunction(test);
RegisterBrewFunction(time);
根据命令行参数返回对应的函数
static BrewFunction GetBrewFunction(const caffe::string& name) {
if (g_brew_map.count(name)) {
return g_brew_map[name];
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "Available caffe actions:";
for (BrewMap::iterator it = g_brew_map.begin();
it != g_brew_map.end(); ++it) {
LOG(ERROR) << "\t" << it->first;
}
LOG(FATAL) << "Unknown action: " << name;
return NULL; // not reachable, just to suppress old compiler warnings.
}
}
Training
caffe train learns models from scratch, resumes learning from saved snapshots, and fine-tunes models to new data and tasks:
- All training requires a solver configuration through the
-solver solver.prototxtargument. - Resuming requires the
-snapshot model_iter_1000.solverstateargument to load the solver snapshot. - Fine-tuning requires the
-weights model.caffemodelargument for the model initialization.
例如:
# train LeNet
caffe train -solver examples/mnist/lenet_solver.prototxt
# train on GPU 2
caffe train -solver examples/mnist/lenet_solver.prototxt -gpu 2
# resume training from the half-way point snapshot
caffe train -solver examples/mnist/lenet_solver.prototxt -snapshot examples/mnist/lenet_iter_5000.solverstate
int train() {
CHECK_GT(FLAGS_solver.size(), 0) << "Need a solver definition to train.";
CHECK(!FLAGS_snapshot.size() || !FLAGS_weights.size())
<< "Give a snapshot to resume training or weights to finetune "
"but not both.";
vector<string> stages = get_stages_from_flags();
caffe::SolverParameter solver_param;
caffe::ReadSolverParamsFromTextFileOrDie(FLAGS_solver, &solver_param);
solver_param.mutable_train_state()->set_level(FLAGS_level);
for (int i = 0; i < stages.size(); i++) {
solver_param.mutable_train_state()->add_stage(stages[i]);
}
// If the gpus flag is not provided, allow the mode and device to be set
// in the solver prototxt.
if (FLAGS_gpu.size() == 0
&& solver_param.has_solver_mode()
&& solver_param.solver_mode() == caffe::SolverParameter_SolverMode_GPU) {
if (solver_param.has_device_id()) {
FLAGS_gpu = "" +
boost::lexical_cast<string>(solver_param.device_id());
} else { // Set default GPU if unspecified
FLAGS_gpu = "" + boost::lexical_cast<string>(0);
}
}
vector<int> gpus;
get_gpus(&gpus);
if (gpus.size() == 0) {
LOG(INFO) << "Use CPU.";
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::CPU);
} else {
ostringstream s;
for (int i = 0; i < gpus.size(); ++i) {
s << (i ? ", " : "") << gpus[i];
}
LOG(INFO) << "Using GPUs " << s.str();
#ifndef CPU_ONLY
cudaDeviceProp device_prop;
for (int i = 0; i < gpus.size(); ++i) {
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&device_prop, gpus[i]);
LOG(INFO) << "GPU " << gpus[i] << ": " << device_prop.name;
}
#endif
solver_param.set_device_id(gpus[0]);
Caffe::SetDevice(gpus[0]);
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::GPU);
Caffe::set_solver_count(gpus.size());
}
caffe::SignalHandler signal_handler(
GetRequestedAction(FLAGS_sigint_effect),
GetRequestedAction(FLAGS_sighup_effect));
if (FLAGS_snapshot.size()) {
solver_param.clear_weights();
} else if (FLAGS_weights.size()) {
solver_param.clear_weights();
solver_param.add_weights(FLAGS_weights);
}
shared_ptr<caffe::Solver<float> >
solver(caffe::SolverRegistry<float>::CreateSolver(solver_param));
solver->SetActionFunction(signal_handler.GetActionFunction());
if (FLAGS_snapshot.size()) {
LOG(INFO) << "Resuming from " << FLAGS_snapshot;
solver->Restore(FLAGS_snapshot.c_str());
}
LOG(INFO) << "Starting Optimization";
if (gpus.size() > 1) {
#ifdef USE_NCCL
caffe::NCCL<float> nccl(solver);
nccl.Run(gpus, FLAGS_snapshot.size() > 0 ? FLAGS_snapshot.c_str() : NULL);
#else
LOG(FATAL) << "Multi-GPU execution not available - rebuild with USE_NCCL";
#endif
} else {
solver->Solve();
}
LOG(INFO) << "Optimization Done.";
return 0;
}
Testing
# score the learned LeNet model on the validation set as defined in the
# model architeture lenet_train_test.prototxt
caffe test -model examples/mnist/lenet_train_test.prototxt -weights examples/mnist/lenet_iter_10000.caffemodel -gpu 0 -iterations 100
Benchmarking
# time LeNet training on CPU for 10 iterations
caffe time -model examples/mnist/lenet_train_test.prototxt -iterations 10
# time LeNet training on GPU for the default 50 iterations
caffe time -model examples/mnist/lenet_train_test.prototxt -gpu 0
# time a model architecture with the given weights on the first GPU for 10 iterations
caffe time -model examples/mnist/lenet_train_test.prototxt -weights examples/mnist/lenet_iter_10000.caffemodel -gpu 0 -iterations 10
Diagnostics
# query the first device
caffe device_query -gpu 0
Parallelism
# train on GPUs 0 & 1 (doubling the batch size)
caffe train -solver examples/mnist/lenet_solver.prototxt -gpu 0,1
# train on all GPUs (multiplying batch size by number of devices)
caffe train -solver examples/mnist/lenet_solver.prototxt -gpu all
Python
pycaffe是caffe的python接口
- 主要的API有:
-
caffe.Netis the central interface for loading, configuring, and running models.caffe.Classifierandcaffe.Detectorprovide convenience interfaces for common tasks. -
caffe.SGDSolverexposes the solving interface. -
caffe.iohandles input / output with preprocessing and protocol buffers. -
caffe.drawvisualizes network architectures. -
Caffe blobs are exposed as numpy ndarrays for ease-of-use and efficiency.
-
源代码中提供了ipython nobebook案例,在caffe/examples/路径下
参考资料
- https://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/tutorial/
- http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/
- https://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/tutorial/convolution.html
